In the world of Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE), meshing plays a fundamental role in ensuring accurate and reliable simulation results. Whether in Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), or Electromagnetic Simulations, the quality of the mesh directly impacts the precision, efficiency, and convergence of the simulation.
What is Meshing?
Meshing is the process of discretizing a continuous geometry into smaller elements (such as tetrahedrons, hexahedrons, quadrilaterals, or triangles) to facilitate numerical analysis. This enables CAE software to approximate real-world physical behavior by solving mathematical equations for each element.
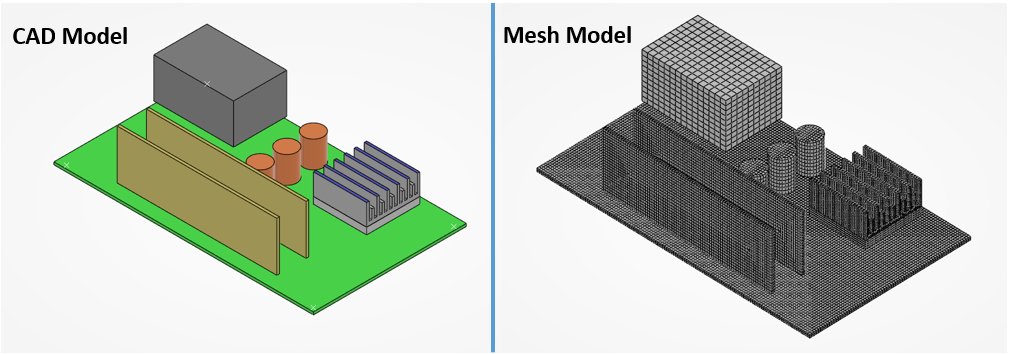
Types of Meshes:
Commonly, meshes are categorized as:
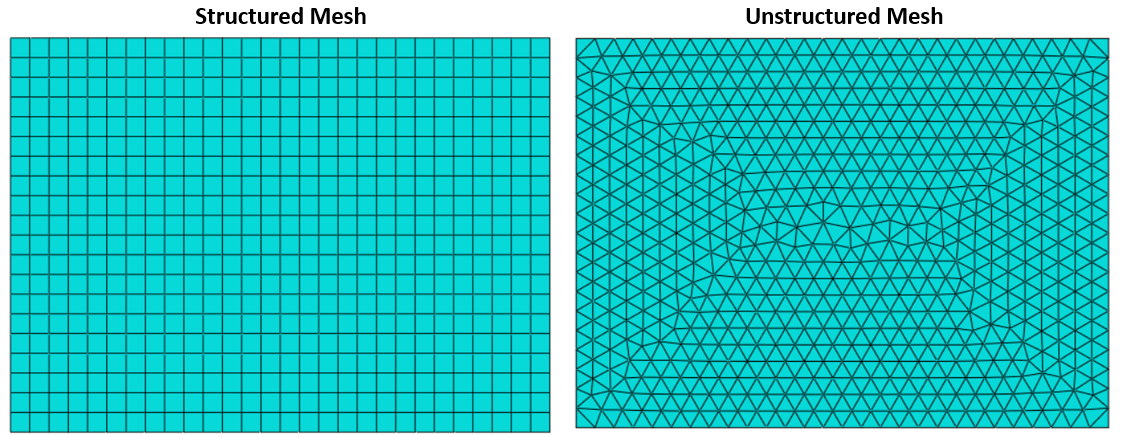
- Structured meshes: A structured mesh features a systematically arranged grid of cells, typically composed of quadrilaterals in two dimensions and hexahedra in three dimensions. The cell edges are generally parallel, with a uniform grid spacing throughout.
- Unstructured meshes: Unstructured meshes, in contrast, consist of an irregular arrangement of grid cells that can vary in shape and size. In two dimensions, the cells may be quadrilaterals or triangles, while in three dimensions, they can be hexahedra or tetrahedra. The grid spacing is non-uniform, allowing greater flexibility in capturing complex geometries.
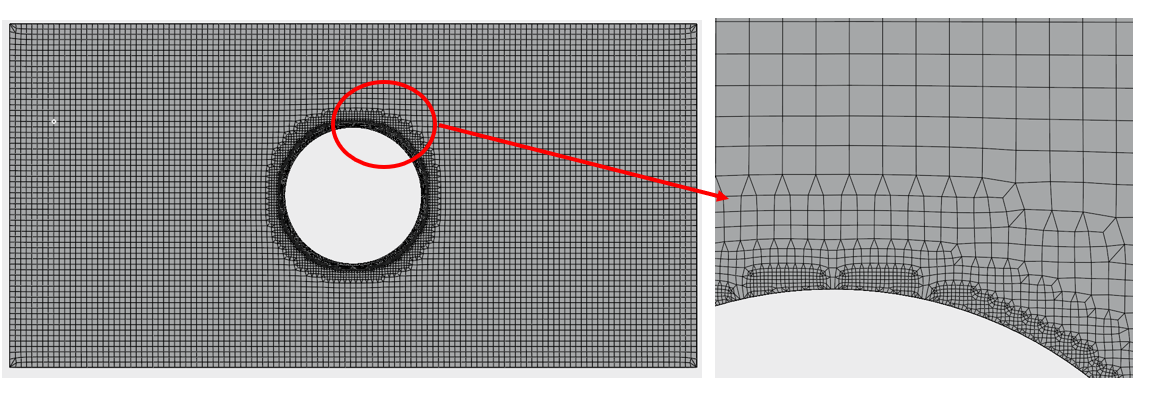
- Hybrid Mesh: A hybrid mesh is a combination of different mesh types, incorporating both structured and unstructured elements to optimize accuracy and computational efficiency. It typically includes hexahedral, tetrahedral, prismatic, or pyramidal elements, allowing for better resolution in critical areas while maintaining flexibility in complex geometries.
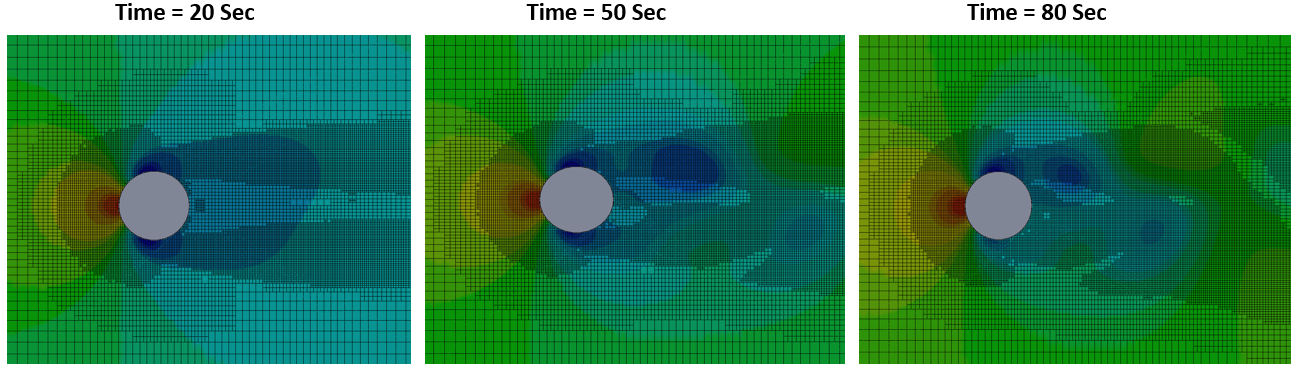
- Adaptive Mesh: An adaptive mesh is a type of mesh that dynamically refines or coarsens during a simulation based on predefined criteria, such as error estimation, gradients, or solution accuracy. This approach improves computational efficiency by increasing resolution in critical regions while reducing element density in less important areas.
Why is Meshing Important?
- Accuracy of Simulations
A well-defined mesh ensures that the numerical solution closely approximates real-world physics. Finer meshes in critical regions capture sharp gradients, stress concentrations, and turbulence, leading to higher accuracy in CAE simulations. Poor meshing can lead to misleading results, impacting design decisions. - Computational Efficiency
While finer meshes improve accuracy, they also increase computational cost. A balance between mesh density and computation time is crucial. Adaptive meshing techniques, such as h-refinement (increasing element count) and p-refinement (increasing element order), help optimize performance. - Convergence and Stability
A well-structured mesh ensures better convergence in CAE solvers. Poor-quality meshes with highly skewed or distorted elements can cause numerical instabilities, leading to slow or non-converging solutions. - Structural stress distribution in FEA
- Turbulent flow modeling in CFD
- Thermal and electromagnetic fields in Multiphysics simulations
- Cost and Time Savings
High-quality meshing reduces the need for excessive rework and reruns, leading to faster product development cycles and lower simulation costs.
Best Practices for Effective Meshing
- Use Refinement in High-Gradient Regions
Refine the mesh in areas with sharp variations, such as stress concentrations and boundary layers, to improve accuracy. - Avoid Highly Distorted Elements
Poorly shaped elements can cause numerical errors; maintaining good element quality enhances solver performance and stability. - Utilize Mesh Convergence Studies
Gradually refine the mesh and compare results to ensure accuracy without excessive computational cost. - Select Appropriate Element Types
Use hexahedral elements for accuracy, tetrahedral for complex geometries, and prismatic/pyramidal where needed. - Consider Adaptive Meshing
Dynamically refine critical regions while coarsening less important areas to balance accuracy and efficiency.
Conclusion:
Meshing is a critical aspect of CAE simulations, directly impacting accuracy, efficiency, and computational performance. A well-structured mesh ensures reliable results while optimizing resource usage. Poor meshing can lead to errors, instability, and longer processing times. Advanced meshing techniques, such as adaptive and hybrid meshing, help balance precision and efficiency. Mastering meshing strategies is essential for improving simulation quality and driving better engineering decisions.
We Urge You To Call Us For Any Doubts & Clarifications That You May Have. We Are Eager to Talk To You
Call Us: +91 7406663589
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()